Step into the world of bonded leather, where appearances can be deceiving and quality is often sacrificed for affordability.
While marketed as a budget-friendly alternative to real leather, bonded leather hides a sinister secret beneath its smooth exterior.
Prepare to uncover the truth behind this synthetic imposter and discover why it falls short in durability, sustainability, and overall value.
What is Bonded Leather?
Bonded leather is a thin, leather alternative that is a combination of waste leather and plastics.
Bonded leather is commonly marketed as a more affordable alternative to genuine leather.
However, it's important to understand that bonded leather is not actually a true leather product.
Instead, it is a man-made material composed of a combination of shredded or ground-up leather scraps and synthetic materials such as polyurethane (PU) or vinyl.
Bonded leather is not a true faux leather, synthetic leather or artificial leather like PU leather. And it’s not a true real leather like full grain leather either. It sits somewhere in the middle.
These components are bonded together using adhesives to create sheets or rolls of bonded leather material to effectively create a reconstituted leather.
The real leather content is usually very small.
This type of leather is extremely susceptible to peeling and flaking because of how it is made, and because of this, it is often cheap to buy.
Is Bonded Leather Real Leather?
Bonded leather is not real leather and is commonly referred to as fake leather, leathersoft or vinyl leather.
Bonded leather is also not the same as 100% PU vegan leather.
Bonded leather cannot be considered vegan due to the small amount of real leather content.
Even though it does contain some small fibres from real leather, it is mostly made up of plastics and synthetic materials.
The small quantities of fiber and leather scraps are not enough to ensure the quality of the material.
Bonded leather is easily distinguishable from real leather because of its texture and plastic appearance.

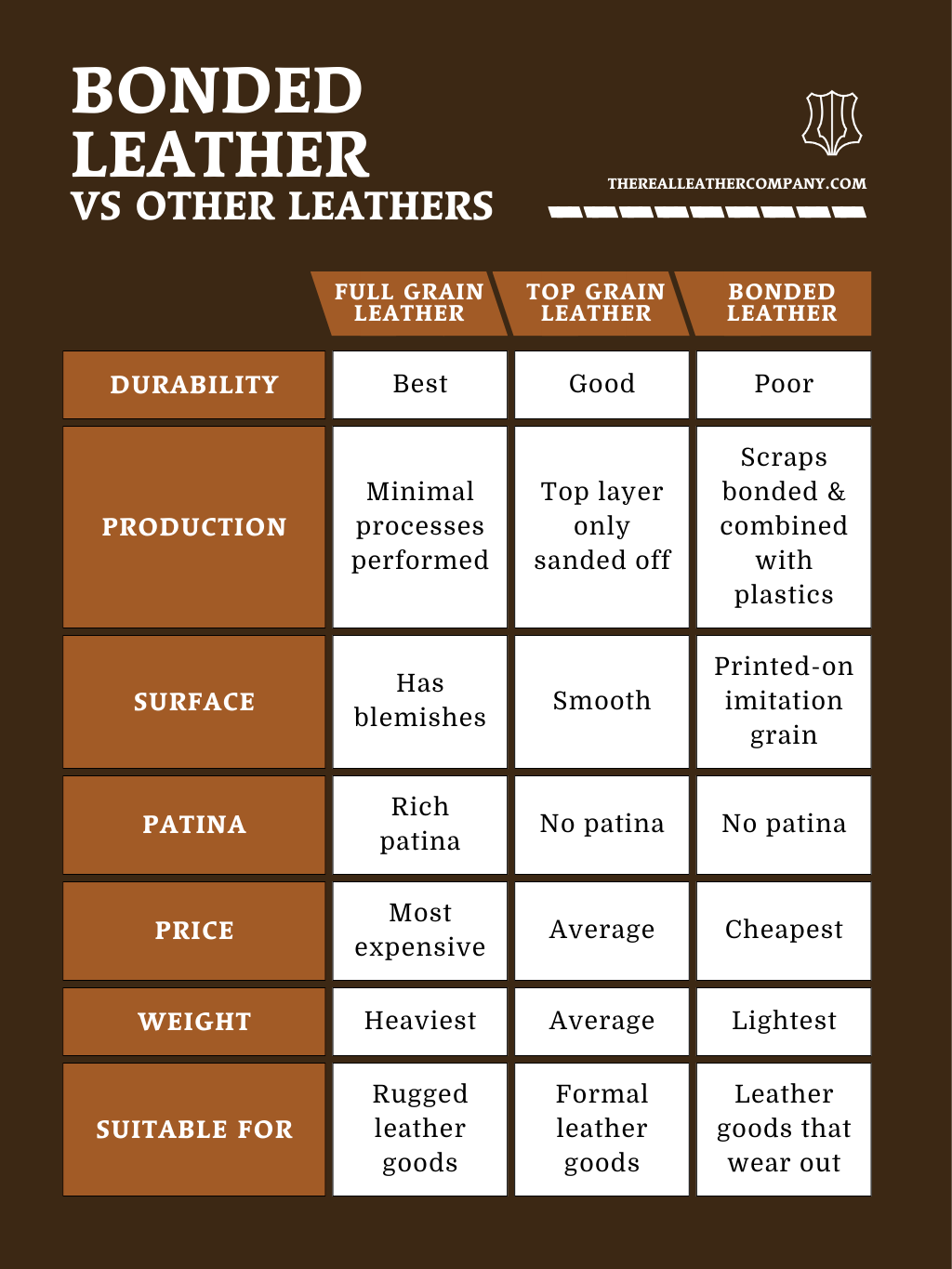
Bonded Leather vs Real Leather
Deluxe materials like real leather have been key to the fashion and lifestyle industries for decades.
The appeal of real leather is hard to deny, with its unique blend of visual and durable properties, it’s not hard to see why real leather goods are such high-quality and so long-lasting.
Many think that environmentally, real leather is much more sustainable than bonded leather, even though bonded leather can be made of recycled materials.
Real leather bags can often last a lifetime and are considered to be a much more durable product.
To match the lifetime of a real leather good you would expect to buy a bonded leather good several times, and even then you may fall short.
In reality, bonded leather is not even comparable.
It cannot beat real leather in quality, durability or even aesthetic appeal and whilst it is seemingly more affordable, with replacement products necessary very often, this thin fake leather is no match for the quality of real leather products.

How to Spot Bonded Leather
While bonded leather may resemble real leather at first glance, there are several telltale signs that can help you identify it.
These steps often reveal its inferior quality compared to genuine leather. Here are some key indicators to look out for:
1. Lack of Natural Characteristics
Bonded leather typically lacks the natural imperfections and variations found in genuine leather, such as grain patterns, wrinkles, and scars.
Instead, it may have a more uniform appearance, lacking the depth and richness that genuine leather possesses.
2. Texture and Feel
Run your fingers across the surface of the material. Bonded leather often feels smoother and less supple than genuine leather.
It may have a plasticky or synthetic texture (a bit like bicast leather), lacking the softness and warmth that are characteristic of real leather.
3. Peeling
Over time, bonded leather is prone to peeling, cracking, and delamination, especially in areas of frequent use or stress.
Check for any signs of flaking or separation between layers, which are common issues with bonded leather products as the synthetic components degrade.
4. Backing Material
Examine the edges or underside of the material to see if there is a visible backing material, such as fabric or paper backing
Genuine leather typically does not have a separate backing layer, while bonded leather often does, as it is manufactured by bonding shredded leather particles to a backing material.
5. Smell Test
Although not always reliable, genuine leather has a distinct, earthy smell that is often absent in bonded leather products.
Bonded leather may have a chemical or artificial odor due to the synthetic materials used in its production.

Advantages of Bonded Leather
1. Affordability
One of the primary advantages of bonded leather is its lower cost compared to genuine leather products.
Bonded leather offers a more budget-friendly option for consumers who desire the look of leather without the higher price tag.
2. Uniform Appearance
Bonded leather can be manufactured to have a consistent appearance, texture, and color.
This uniformity makes it easier to match and coordinate with other decor or accessories.
This often makes this material a good choice for home furnishings like bonded leather sofas or in other upholstery material.
3. Eco-Friendly Use of Scraps
Bonded leather often utilizes recycled scraps of leather from the manufacturing process of genuine leather goods.
By repurposing these scraps, bonded leather contributes to reducing waste and promoting sustainability in the leather industry.
4. Variety of Designs
Bonded leather can be embossed, dyed, or treated to mimic various textures and patterns, offering a wide range of design possibilities.
This versatility allows manufacturers to create bonded leather products with different visual effects to suit diverse consumer preferences.
Disadvantages of Bonded Leather
1. Durability Issues
The most significant drawback of bonded leather is its limited durability compared to real leather.
The bonding process and synthetic components can lead to premature wear and tear, including peeling, cracking, and delamination, especially with prolonged use or exposure to environmental factors.
2. Lack of Breathability
Unlike genuine leather, bonded leather lacks the natural breathability and moisture-wicking properties that contribute to comfort when used in upholstery or clothing.
As the good is not 100% real leather and is treated, no patina will develop. This is a major factor for those that value high quality leathers.
This may result in a less comfortable or less breathable experience for users, especially in warm or humid conditions.
3. Shorter Lifespan
Due to its composition and manufacturing process, bonded leather typically has a shorter lifespan than genuine leather products.
Over time, bonded leather may deteriorate more quickly, requiring replacement sooner than higher-quality leather alternatives.
4. Limited Value Retention
While genuine leather products often retain their value and can be considered investments, bonded leather items are less likely to hold their value over time.
Their lower quality and susceptibility to damage can diminish their resale or longevity as heirloom pieces.

Is Bonded Leather Environmentally Friendly?
When considering the environmental impact of bonded leather, it's essential to recognize that while it may be marketed as a sustainable option due to its use of recycled leather scraps, its overall environmental footprint is far from ideal.
Here's why:
1. High Synthetic Content
Bonded leather contains a significant proportion of synthetic materials such as polyurethane (PU) or vinyl, which are derived from non-renewable resources and can have negative environmental consequences.
The production and disposal of these synthetic components contribute to pollution and resource depletion.
2. Limited Durability
Unlike genuine leather, which can last for decades with proper care, bonded leather tends to have a shorter lifespan and is more prone to damage and deterioration.
As a result, bonded leather products may need to be replaced more frequently, leading to increased waste generation and resource consumption over time.
3. Chemical Use
The manufacturing process of bonded leather involves the use of adhesives and chemicals to bond the shredded leather particles with synthetic materials.
These chemicals can be harmful to both human health and the environment, contributing to air and water pollution during production and disposal.
4. End-of-Life Disposal
When bonded leather products reach the end of their lifespan, they are often not biodegradable due to the synthetic components.
As a result, they may end up in landfills, where they can take hundreds of years to decompose, further contributing to environmental pollution and degradation.

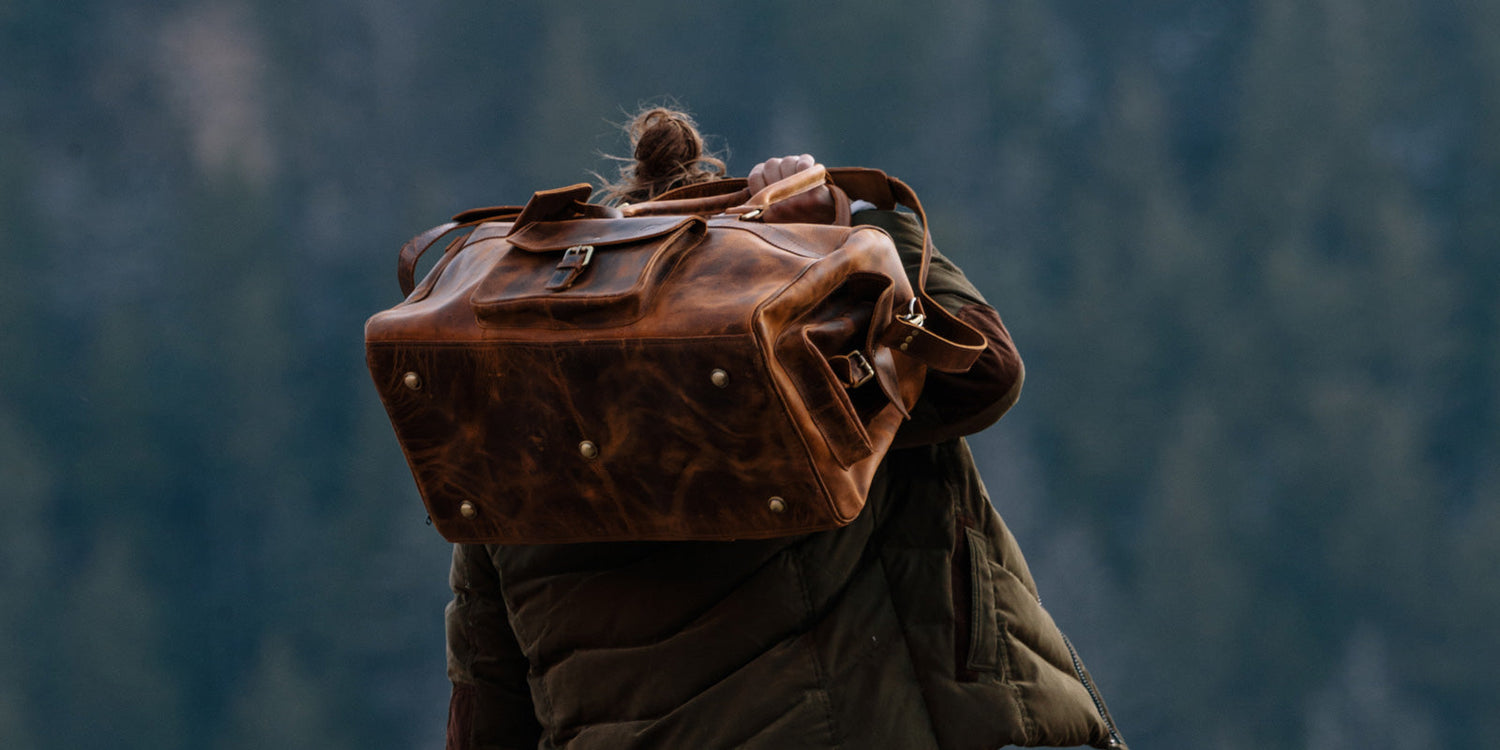
Why we Recommend Genuine Leathers for Bags
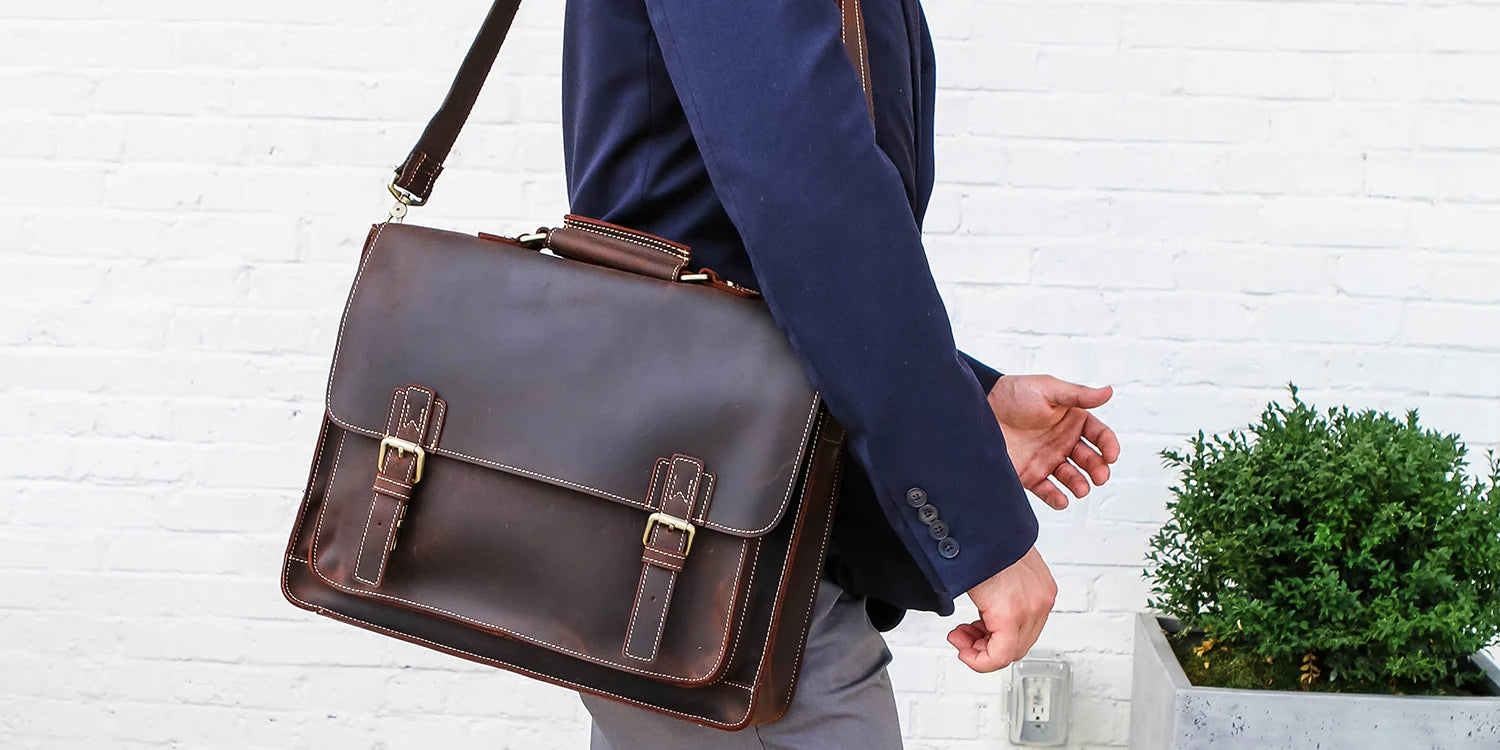
We always recommend full grain and top grain leather, particularly for products that see a lot of wear, like leather bags.
We understand the appeal of cheap, fake or low percentage leathers but the quality and longevity of real leather goods really speaks for itself.
Bags generally see a lot of use.
Travel bags, briefcases and backpacks are some of the heaviest wear items you can use.
You can avoid repeat buying by purchasing a one-off high-quality item whether its for yourself or as a gift, and be able to enjoy a full grain or top grain leather product for many years.
At The Real Leather Company, you can check out our extensive collections of real leather goods.
Checkout in confidence, knowing you’ve got free shipping a 30 day returns window.
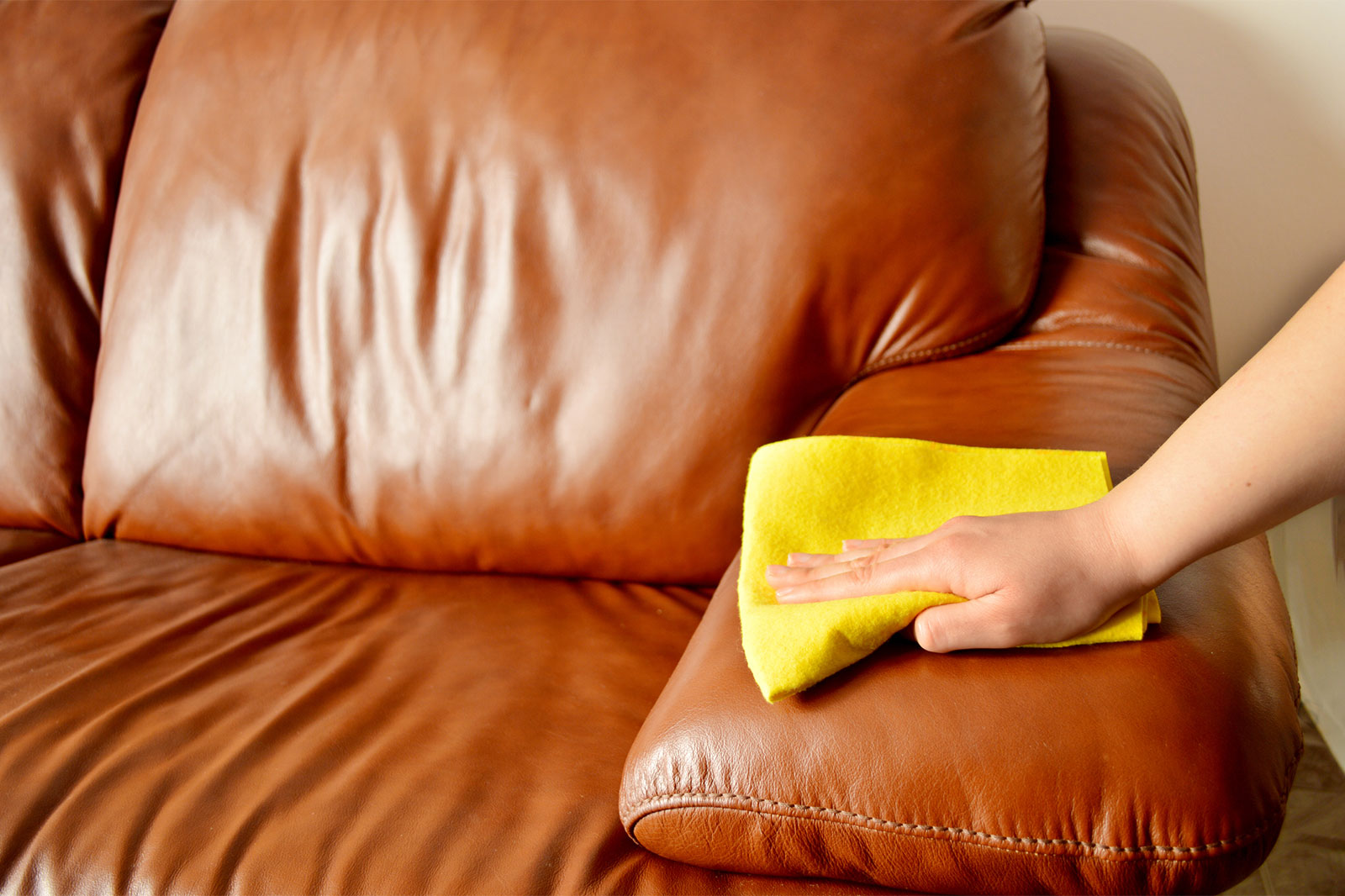
How to Clean Bonded Leather
Bonded leather's high plastic content makes it easy to wipe down and clean, but the lack of quality in the material can mean it’s prone to splitting, scratching, and wearing.
Here are a few tips on how you can clean bonded leather.
For dirt and other surface-level marks, you should be able to wipe down bonded leather with a soft damp cloth.
For dried or more stubborn stains, warm water should help.
You can also use a soft brush to remove stains but you should be careful not to scratch bonded leather as it is very susceptible to damage.
Because it is cheaply made, damage to the material will make it look far worse and can mean the whole product needs replacing.
Bonded leather is much more fragile than real leather and that makes leather care more challenging.
We don’t recommend using standard leather conditioner on bonded leather. As the leather percentage is often so low this can do more harm than good.
We advise against using abrasive brushes or sponges or strong cleaning solutions as these will likely damage your bonded leather product.
Similarly, keep out of direct sunlight for prolonged periods as this can also dry out and crack bonded leather.

How is Bonded Leather Produced?
The production process of bonded leather involves a combination of recycled leather leftover scraps and synthetic materials to create a leather-like composite material.
While the specifics may vary slightly between manufacturers, the general steps typically include the following:
1. Collection
In the initial stage of bonded leather production, leather scraps are collected from various sources such as tanneries, leather goods manufacturers, and upholstery workshops.
These scraps may include remnants leftover from the production of natural leather items, ensuring a sustainable use of materials.
2. Preparation
Once the leather scraps are gathered, they undergo a preparation process where they are shredded or ground into smaller pieces.
This step helps to break down the leather into fine particles, making it easier to blend with the synthetic binders that will hold the material together.
3. Bonding
After the leather scraps are prepared, they are mixed with polyurethane binders.
These binders serve as adhesive agents, effectively bonding the shredded leather particles together and adhering them to a backing material, typically a fabric or paper substrate.
4. Formation
The bonded mixture of leather and binders is then pressed and dried to form sheets or rolls of bonded leather material.
This process involves applying heat and pressure to compact the materials and ensure proper bonding, resulting in a smooth and uniform surface.
5. Finishing
Once the bonded leather sheets are formed, they may undergo various finishing treatments to enhance their appearance, texture, and durability.
This can include embossing to create a desired texture, dyeing to add color, and applying protective coatings to improve resistance to wear and tear.
6. Quality Assurance
Throughout the production process, stringent quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the bonded leather meets specified standards for strength, appearance, and consistency.
This may involve regular inspections, testing for durability, and adjustments to optimize the final product.

FAQs
1. What is bonded leather?
Bonded leather is a material made by combining shredded or ground-up leather scraps with synthetic materials such as polyurethane or vinyl.
It is often used as a more affordable alternative to genuine leather.
2. How does bonded leather differ from genuine leather?
Unlike genuine leather, which is made from animal hides, bonded leather contains a lower percentage of actual leather fibers and relies on synthetic binders for cohesion.
This results in differences in durability, texture, and overall quality.
3. Is bonded leather durable?
While bonded leather may initially resemble genuine leather, it tends to have a shorter lifespan and is more prone to issues such as peeling, cracking, and delamination.
Genuine leather typically offers greater durability and longevity with proper care.
4. Is bonded leather environmentally friendly?
Bonded leather's environmental impact is debated.
While it may utilize recycled leather scraps, its reliance on synthetic materials and chemical processes raises concerns about its sustainability.
Genuine leather sourced from responsible practices may offer a more environmentally friendly option.
5. How can I tell if a product is made of bonded leather?
Bonded leather can often be identified by its lack of natural characteristics, smoother texture, and the presence of a separate backing material.
It may also exhibit signs of peeling or delamination over time.
6. What are the advantages of bonded leather?
Bonded leather is typically more affordable than genuine leather and can offer a uniform appearance.
It also allows for the repurposing of leather scraps, contributing to waste reduction.
7. What are the disadvantages of bonded leather?
Some drawbacks of bonded leather include its limited durability, lack of breathability, and shorter lifespan compared to genuine leather.
It may also lack the value retention and environmental benefits associated with genuine leather.
8. How should I care for bonded leather products?
Bonded leather products should be cleaned and maintained according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Some leathers like suede will have special manufacturer care instructions.
Avoid exposing them to excessive heat or moisture, which can accelerate deterioration.
9. Can bonded leather be repaired?
While minor repairs may be possible for bonded leather products, significant damage such as peeling or delamination may be challenging to fix effectively.
It is often more cost-effective to replace damaged items rather than attempting repairs.
10. Is bonded leather suitable for all applications?
This material may be suitable for certain applications such as bookbinding, upholstery, bonded leather furniture, books and bibles, or fashion accessories.
But for items you’d like to last a long time, like wallets, handbags and briefcases, bonded leather is unlikely to be suitable.
However, its limitations in terms of durability and quality should be taken into account when making purchasing decisions.

























